Digital Transformation, zBlog
What is Enterprise Architecture? Exploring the Foundations
atif | Updated: April 19, 2024

Introduction
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a comprehensive framework for managing and aligning an organization’s business processes, information, applications, and infrastructure to achieve its goals and objectives. It provides a holistic view of the organization, enabling it to make informed decisions and optimize its resources.
The primary purpose of enterprise architecture is to bridge the gap between an organization’s strategic goals and its day-to-day operational activities. By aligning these elements, EA helps organizations improve their efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance their competitive advantage.
The Importance of Enterprise Architecture

In today’s complex and rapidly changing business landscape, organizations face a variety of challenges, including:
- 1. Increasing competition: Businesses must constantly adapt to stay ahead of their competitors, requiring agile and responsive systems.
- 2. Emerging technologies: New technologies, such as cloud computing, big data, and the Internet of Things (IoT), are transforming the way organizations operate and interact with their customers.
- 3. Regulatory compliance: Organizations must navigate an ever-changing regulatory environment, ensuring that their systems and processes comply with relevant laws and industry standards.
- 4. Organizational silos: Many organizations struggle with communication and collaboration between different departments, leading to inefficiencies and duplication of effort.
Enterprise architecture addresses these challenges by providing a comprehensive framework that aligns an organization’s people, processes, and technology to support its strategic goals. By doing so, EA can help organizations:
- 1. Improve decision-making: EA provides a holistic view of the organization, enabling leaders to make informed decisions that consider the interdependencies between different business and IT components.
- 2. Enhance operational efficiency: By identifying and eliminating redundancies, EA can help organizations streamline their processes and reduce costs.
- 3. Increase agility and responsiveness: EA enables organizations to quickly adapt to changes in the market, technology, or regulatory environment, allowing them to seize new opportunities and stay ahead of the competition.
- 4. Enhance collaboration and communication: EA promotes a shared understanding of the organization’s goals, processes, and technologies, fostering better collaboration and communication across different departments.
The Core Elements of Enterprise Architecture

Enterprise architecture consists of several core elements that work together to create a comprehensive view of the organization:
- 1. Business architecture: This component defines the organization’s strategic goals, business processes, and organizational structure. It helps align the business with the overall objectives of the organization.
- 2. Data architecture: This element focuses on the organization’s data assets, including the data models, data flows, and data management processes. It ensures that data is effectively managed and utilized across the organization.
- 3. Application architecture: This component deals with the organization’s software applications, their functionality, and their interactions with each other. It helps ensure that the applications support the business processes and data requirements.
- 4. Technology architecture: This element encompasses the organization’s hardware, software, and infrastructure components, including networks, servers, and storage systems. It ensures that the technology infrastructure supports the business and application requirements.
- 5. Security architecture: This component addresses the organization’s security requirements, including access control, data protection, and risk management. It helps ensure that the organization’s assets are protected from cyber threats and other security risks.
The Enterprise Architecture Process
Developing and implementing an effective enterprise architecture involves a structured process that typically includes the following steps:
- 1. Assess the current state: The first step is to analyze the organization’s current business processes, data, applications, and technology infrastructure. This assessment helps identify any gaps or inefficiencies that need to be addressed.
- 2. Define the target state: Based on the organization’s strategic goals and objectives, the enterprise architecture team defines the desired future state, including the target business processes, data, applications, and technology infrastructure.
- 3. Develop the transition plan: The team then creates a detailed plan for transitioning from the current state to the target state, taking into account the organization’s available resources, timelines, and any potential risks or constraints.
- 4. Implement the changes: The transition plan is then executed, with the enterprise architecture team overseeing the implementation of the necessary changes to the organization’s business, data, applications, and technology.
- 5. Monitor and optimize: Once the target state has been achieved, the enterprise architecture team continues to monitor the organization’s performance and make adjustments as needed to ensure that the EA remains aligned with the organization’s evolving needs.
The Role of the Enterprise Architect
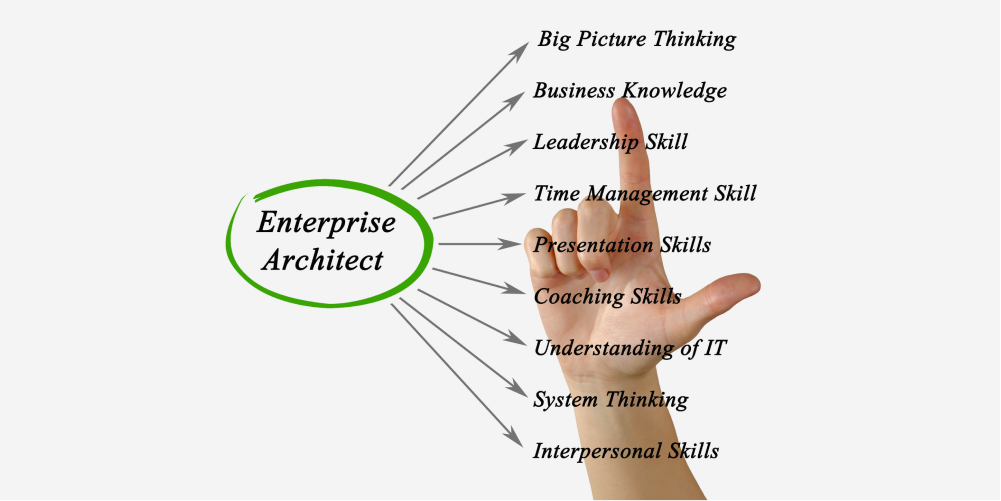
The enterprise architect is the key individual responsible for developing and implementing the organization’s enterprise architecture. The enterprise architect’s responsibilities typically include:
- 1. Aligning business and IT: The enterprise architect acts as a bridge between the organization’s business and IT functions, ensuring that the technology infrastructure supports the business goals and objectives.
- 2. Defining the architectural vision: The enterprise architect is responsible for defining the overall vision and strategy for the organization’s enterprise architecture, taking into account the organization’s current state, future goals, and industry trends.
- 3. Designing the EA framework: The enterprise architect is responsible for designing the specific components of the enterprise architecture, including the business, data, application, and technology architectures.
- 4. Facilitating stakeholder collaboration: The enterprise architect works closely with stakeholders from different departments, including business, IT, and security, to ensure that their requirements and concerns are addressed in the EA.
- 5. Overseeing implementation: The enterprise architect is responsible for overseeing the implementation of the enterprise architecture, ensuring that the transition plan is executed effectively and that the target state is achieved.
- 6. Continuously improving the EA: The enterprise architect is responsible for monitoring the organization’s performance and making adjustments to the enterprise architecture as needed to ensure that it remains aligned with the organization’s evolving needs.
The Benefits of Enterprise Architecture

Implementing an effective enterprise architecture can provide a variety of benefits to organizations, including:
- 1. Improved decision-making: By providing a comprehensive view of the organization, enterprise architecture can help leaders make more informed and strategic decisions.
- 2. Enhanced operational efficiency: EA can help organizations streamline their processes, reduce redundancies, and optimize their resource allocation, leading to cost savings and improved productivity.
- 3. Increased agility and responsiveness: EA enables organizations to quickly adapt to changes in the market, technology, or regulatory environment, allowing them to seize new opportunities and stay ahead of the competition.
- 4. Improved alignment between business and IT: EA helps ensure that the organization’s technology infrastructure is aligned with its business goals and objectives, enabling more effective collaboration and communication between the two functions.
- 5. Enhanced data management and integration: EA can help organizations better manage and integrate their data assets, improving the quality and availability of information for decision-making.
- 6. Improved security and risk management: EA can help organizations identify and mitigate security risks, ensuring that their systems and processes are secure and compliant with relevant regulations.
The Evolution of Enterprise Architecture

Enterprise architecture has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1980s. Initially, EA was primarily focused on aligning IT infrastructure with business requirements. Over time, however, the scope of EA has expanded to encompass a more holistic view of the organization, including its people, processes, and technology.
Today, enterprise architecture is increasingly focused on enabling digital transformation, as organizations seek to leverage emerging technologies such as cloud computing, big data, and the Internet of Things to improve their operations and enhance their customer experience.
As the business landscape continues to evolve, enterprise architecture will likely continue to adapt and evolve as well. Some key trends in the future of EA include:
- 1. Increased focus on business outcomes: EA will become more closely aligned with the organization’s strategic goals and objectives, with a greater emphasis on delivering tangible business value.
- 2. Greater use of agile and iterative approaches: Enterprise architecture will increasingly adopt agile and iterative development methodologies, enabling organizations to respond more quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs.
- 3. Leveraging emerging technologies: EA will play a crucial role in helping organizations leverage emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things, to improve their operations and enhance their customer experience.
- 4. Increased collaboration and cross-functional integration: EA will become more integrated with other organizational functions, such as business strategy, project management, and change management, to ensure a more holistic approach to organizational transformation.
- 5. Greater emphasis on data governance and analytics: EA will place a stronger emphasis on data governance and analytics, enabling organizations to make more informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, enterprise architecture is a powerful and dynamic framework for aligning an organization’s people, processes, and technology to support its strategic goals. As the business landscape continues to evolve, EA will likely play an increasingly critical role in enabling organizations to navigate the challenges and seize the opportunities of the digital age.
Trantor has truly embraced the power of enterprise architecture. Our commitment to enterprise architecture has enabled us to anticipate and respond to changes in the market and leverage emerging technologies. At the heart of Trantor’s enterprise architecture is a highly sophisticated and integrated system that connects the organization’s various service offerings, data assets, and technology infrastructure. By aligning these elements, Trantor has been able to streamline its operations, improve its decision-making, and enhance customer experience – all while maintaining a strong focus on security and compliance.
Trantor has been able to leverage its deep understanding of enterprise architecture to help its clients transform their organizations. By providing expert consulting and implementation services, Trantor has enabled businesses across a wide range of industries to harness the power of EA and drive their digital transformations.




